Molecular mechanisms: Autism gene regulates brain structure
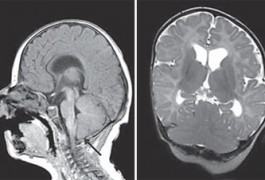
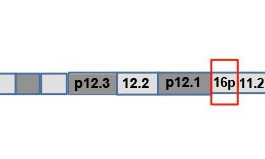
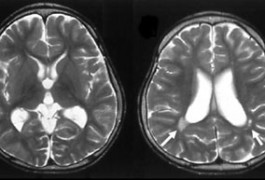
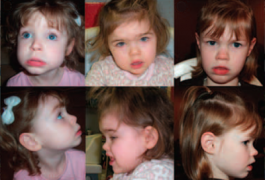
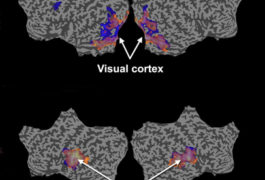
Loss of one copy of TBR1, an autism-linked gene involved in fetal brain development, leads to brain malformations, according to a study published in the September issue of Molecular Syndromology.