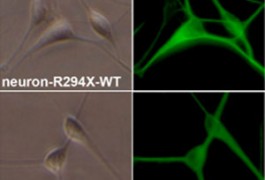
The value of blood cells in autism research
Blood from individuals with autism could help researchers identify biomarkers to diagnose the disorder and learn more about related symptoms, such as gastrointestinal complaints, says molecular biologist Valerie Hu.